Its a cloud computing platform which provide usage based subscription
Why use AWS ?
As buying and maintaining the servers is very expensive.
With AWS you don't need to buy servers , you can rent them based on your usage
AWS supports globally by supporting 18 geographical regions.
So cloud computing is nothing but use of remote servers to manage, store and process the data rather than having local servers
Different Domains in AWS
Compute is Ec2 (Elastic Computing Cloud) , its just like a new Server
Migration When data needs to be migrated from your company warehouse to AWS infrastructure
Security and Identity Compliance: IAM(identity Access Manager), authenticate , manager users on AWS, all permissions are controlled here
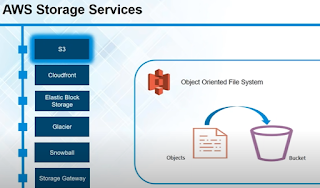
Storage: S3 (Simple Storage Service)
Network and Content Delivery: Route 53, it redirect your application for example: From Go Daddy to AWS infrastructre. So remembering all the IP address of the servers to which the traffic needs to be send will be its Job.
Messaging: It is used to send emails to notify users
Database: RDS(Relational Database System) It can manage database like mysql, PostgreSQL
Management Tools: You can manage all AWS resources example: aws cloudwatch
EC2
These provide webservers which can be customized based on the usage and they are Resizable based on the needs
Lambda
Lambda re used to perform background tasks.
They are not used to host an application
So consider an example you need to apply filters to an image which is kept under S3.
So lambda can be used to perform and apply any filters to that image, provided lambda has that desired code what operation we want to perform
Elastic Beanstalk
Deploy your application without worrying about underlying hardware
This is used to host an application.
Its an automated form of EC2.
In EC2 you need to setup the environment like if you want to install PHP Application, you need to setup PHP in EC2
But In Elastic Beanstalk, you don't need to configure manually, you need to simply select what kind of environment you need.AWS will take care of all things
For certain cases if your technology is not present in Elastic Beanstalk , you can switch to EC2 and create your own environment.
Elastic Load Balancer
It distributes the load on all the deployed instances
AutoScaling
Scale up and Down automatically
We setup metrics.
For example we can say whenever cpu goes beyond 70%, launch a new server, then traffic will be distributed among all these instances and if traffic goes below 10% we scale down that server
LOAD BALANCER AND AUTO SCALING should be utilized together
For Creating a new EC2
1.)Click Ec2 under Compute
2.) Click on Launch Instance
3.) Select AMI(Amazon Machine Image) (i.e. Select OS, red hat,ubuntu, windows server)
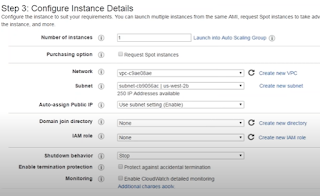
4.) Configure Instance Details
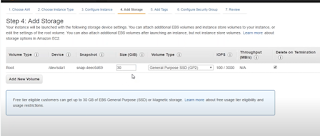
5.) Add Storage
6.) Configure Security Group
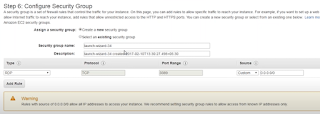
It is used like a firewall to configure Inbound /Outbound traffic
7.) Review the EC2 and Click on Launch
You will be asked to create a key pair
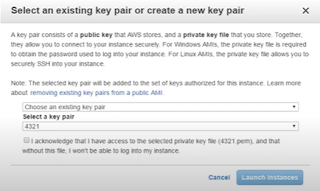
This key will be used to authenticate you with public and private key to access EC2 instance, Public key will be kept in AWS, private key you can download.
Give private key to your console while launching EC2 instance
You can get all details of EC2 from Description i.e. IP Address, instance id
While Logging In, you need to give username and password as private key.
Click on Connect
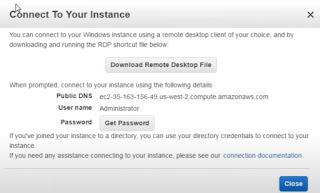
Click get Password
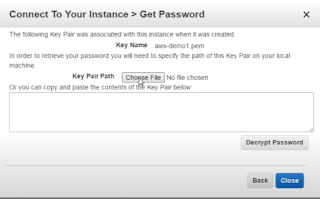
Choose file as your private key and click on Decrypt password
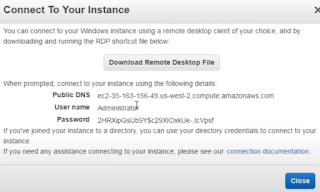
You will see username and Password
How to Access EC2
1.) Launch Remote Desktop Connection
2.) Give IP Address, you can get from Description of EC2
3.) Give Username
4.)Give password that you retrieved above
We need to create a root folder/ bucket in S3 to upload objects
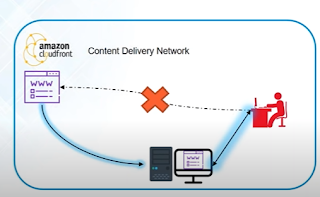
While accessing the application , Content Delivery Network (CloudFront)make sure that the application is cached to nearest location of the user. So that user can access easily with low latency
Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
When you have EC2 your OS will be stored somewhere, so EC2 is backed by EBS
Glacier
When you want to backup the data , you use Glacier, amazon uses magnetic tapes for Glacier
Snowball
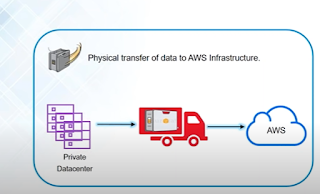
It is used when petabytes of data of huge amount of data needs to be transferred from Data center to AWS
Storage Gateway
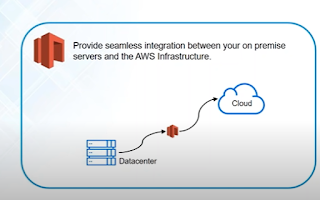
Storage Gateway will sit between your Data center and Cloud, it will keep on taking snapshot of database.
Now lets suppose some corruption has happened on database server, so Storage Gateway will restore that with last snapshot taken
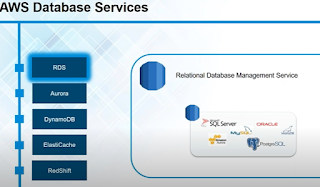
RDS its not a Database but a service that manages Mysql, Oracle, PostgreSQL
It manages services like updating Database Engine, applies patches automatically

It is based on MYSQL, means database built on MYSQL will also run on Aurora but Amazon Aurora is 5 times more faster than MYSQL
Dynamo DB

Non RDBMS are maintained By Dynamo DB, this will also automatically update patches and manage all Non RDBMS
if more data comes, it automatically scales , it grows and shrinks automatically, you don't need to give any size or something
Elastic Cache
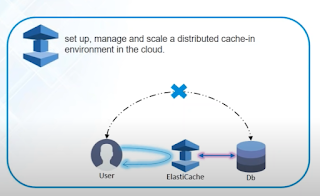
If same query is asked by user again and again, it won't hit db and elastic cache will determine and will store the data in ElasticCache, next time it will be served by Elastic cache
RedShift
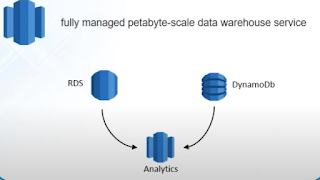
Its an analysis tool that can be used to do analysis of the data present in RDS or DynamoDB
Lets see how this works
Click on RDS

Launch DB instance
Select Engine
For Example, Select Mysql
Select Dev/Test, if you are on lower environments
Select Properties for the DB
Give username and Password for the Database
After that, Click Launch DB Instance
You will get Endpoint after database is Setup

Now we can connect this Mysql from mysql command prompt.
Install Mysql locally and go to Bin directory
Type below command
mysql -h (endpoint) -P (portnumber) -u (username) -p (password)
VPC: Virtual private Cloud
So what we do we keep all database and other AWS resources under VPC, so that they can interact with each other as if they were on its own network
Direct Connect: Its a leased line which directly connects to your AWS Infrastructure.
We use in case bandwidth of our network is not high
Route 53
On Route 53 we enter IP Address of the AWS infrastructure where you want to divert the traffic.
CloudWatch:These tools are used to check if the CPU utilization is more than 80% for an example.
It will trigger an alarm or alert
Cloud Trail: Its a logging service from AWS
Cloud Trail will generate the logs and will store in S3
CLI
It Authenticates to your Amazon Account

I
In VPC Select the value same as of RDS value(to Check Value of RDS, go to RDS and see details)
After Adding Name Servers in DNS
Why use AWS ?
As buying and maintaining the servers is very expensive.
With AWS you don't need to buy servers , you can rent them based on your usage
AWS supports globally by supporting 18 geographical regions.
So cloud computing is nothing but use of remote servers to manage, store and process the data rather than having local servers
Different Domains in AWS

Compute is Ec2 (Elastic Computing Cloud) , its just like a new Server

Migration When data needs to be migrated from your company warehouse to AWS infrastructure
Security and Identity Compliance: IAM(identity Access Manager), authenticate , manager users on AWS, all permissions are controlled here
Storage: S3 (Simple Storage Service)
Network and Content Delivery: Route 53, it redirect your application for example: From Go Daddy to AWS infrastructre. So remembering all the IP address of the servers to which the traffic needs to be send will be its Job.
Messaging: It is used to send emails to notify users
Database: RDS(Relational Database System) It can manage database like mysql, PostgreSQL
Management Tools: You can manage all AWS resources example: aws cloudwatch
EC2
These provide webservers which can be customized based on the usage and they are Resizable based on the needs
Lambda
Lambda re used to perform background tasks.
They are not used to host an application
So consider an example you need to apply filters to an image which is kept under S3.
So lambda can be used to perform and apply any filters to that image, provided lambda has that desired code what operation we want to perform
Elastic Beanstalk
Deploy your application without worrying about underlying hardware
This is used to host an application.
Its an automated form of EC2.
In EC2 you need to setup the environment like if you want to install PHP Application, you need to setup PHP in EC2
But In Elastic Beanstalk, you don't need to configure manually, you need to simply select what kind of environment you need.AWS will take care of all things
For certain cases if your technology is not present in Elastic Beanstalk , you can switch to EC2 and create your own environment.
Elastic Load Balancer
It distributes the load on all the deployed instances
AutoScaling
Scale up and Down automatically
We setup metrics.
For example we can say whenever cpu goes beyond 70%, launch a new server, then traffic will be distributed among all these instances and if traffic goes below 10% we scale down that server
LOAD BALANCER AND AUTO SCALING should be utilized together
For Creating a new EC2
1.)Click Ec2 under Compute
2.) Click on Launch Instance
3.) Select AMI(Amazon Machine Image) (i.e. Select OS, red hat,ubuntu, windows server)
4.) Configure Instance Details

5.) Add Storage

6.) Configure Security Group

It is used like a firewall to configure Inbound /Outbound traffic
7.) Review the EC2 and Click on Launch
You will be asked to create a key pair

This key will be used to authenticate you with public and private key to access EC2 instance, Public key will be kept in AWS, private key you can download.
Give private key to your console while launching EC2 instance
You can get all details of EC2 from Description i.e. IP Address, instance id

While Logging In, you need to give username and password as private key.
Click on Connect

Click get Password

Choose file as your private key and click on Decrypt password

You will see username and Password
How to Access EC2
1.) Launch Remote Desktop Connection
2.) Give IP Address, you can get from Description of EC2
3.) Give Username
4.)Give password that you retrieved above
We need to create a root folder/ bucket in S3 to upload objects

While accessing the application , Content Delivery Network (CloudFront)make sure that the application is cached to nearest location of the user. So that user can access easily with low latency

Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
When you have EC2 your OS will be stored somewhere, so EC2 is backed by EBS
Glacier
When you want to backup the data , you use Glacier, amazon uses magnetic tapes for Glacier
Snowball

It is used when petabytes of data of huge amount of data needs to be transferred from Data center to AWS
Storage Gateway

Storage Gateway will sit between your Data center and Cloud, it will keep on taking snapshot of database.
Now lets suppose some corruption has happened on database server, so Storage Gateway will restore that with last snapshot taken

RDS its not a Database but a service that manages Mysql, Oracle, PostgreSQL
It manages services like updating Database Engine, applies patches automatically

It is based on MYSQL, means database built on MYSQL will also run on Aurora but Amazon Aurora is 5 times more faster than MYSQL
Dynamo DB

Non RDBMS are maintained By Dynamo DB, this will also automatically update patches and manage all Non RDBMS
if more data comes, it automatically scales , it grows and shrinks automatically, you don't need to give any size or something
Elastic Cache

If same query is asked by user again and again, it won't hit db and elastic cache will determine and will store the data in ElasticCache, next time it will be served by Elastic cache
RedShift

Its an analysis tool that can be used to do analysis of the data present in RDS or DynamoDB
Lets see how this works
Click on RDS

Launch DB instance

Select Engine

For Example, Select Mysql

Select Dev/Test, if you are on lower environments
Select Properties for the DB

Give username and Password for the Database
After that, Click Launch DB Instance
You will get Endpoint after database is Setup
Now we can connect this Mysql from mysql command prompt.
Install Mysql locally and go to Bin directory
Type below command
mysql -h (endpoint) -P (portnumber) -u (username) -p (password)
VPC: Virtual private Cloud
So what we do we keep all database and other AWS resources under VPC, so that they can interact with each other as if they were on its own network
Direct Connect: Its a leased line which directly connects to your AWS Infrastructure.
We use in case bandwidth of our network is not high
Route 53
On Route 53 we enter IP Address of the AWS infrastructure where you want to divert the traffic.
CloudWatch:These tools are used to check if the CPU utilization is more than 80% for an example.
It will trigger an alarm or alert
Cloud Formation: This is used when you want to create template of the existing AWS Infrastructure
For example if you want to create a similar environment of your existing AWS Environment, you can SNAPSHOT your existing environmentCloud Trail: Its a logging service from AWS
Cloud Trail will generate the logs and will store in S3
CLI
It Authenticates to your Amazon Account
 |
| This is used when you have large userbase and you want to send Emails(This can be done using SES ) |
SQS: Its a Queue Service, all the tasks are send in a queue to the server
SNS
These are notification service, in which once the task is performed you send Notification to SQS
and then SQS contacts SES to send Email to respective Users
 |
| Sample Architecture of Application in AWS |
We need to authenticate to connect to while uploading files to S3 so we use IAM for authentication purpose
We are using RDS, as we would need some database to store name of the files we are uploading for our record purpose.
In ourcase we are using mysql
Lets Create Elastic Beanstalk
Click on Action> Create Environment
Click on Create Web Server
Select Environment Type
Lets Select PHP and Load Balancing , Auto Scaling
Under Environment Information, provide name of the Environment
You will get a suggested url at which your website will be available,something like (____elasticbeanstalk.com)
Here we are creating environment under VPC, Virtual private cloud, for security purpose
Provide Key pair in Configuration Details
I
In VPC Select the value same as of RDS value(to Check Value of RDS, go to RDS and see details)
Security groups should also be same as of RDS
Lets understand how we migrate Data from our local database to AWS
Take backup of mysql database
mysqldump -u root - p databasename>backup.sql
Here we are exporting the data in backup.sql
Note: Your backup would be stored in bin folder
Lets connect RDS instance and migrate the file over RDS
In Command Line: type below command
mysql -h (hostname, this you will get in your RDS console, under Endpoint Section) -P 3306 -u username -p password
Now you will be connected to mysql RDS instance
1.)Create database Name
2.)Now import the data
mysql -h (hostname, this you will get in your RDS console, under Endpoint Section) -P 3306 -u username -p databaseName < backup.sql
Note: Here we are using same file backup.sql that we exported above and we are importing this file to our Database (databaseName )
Lets connect to RDS and see if the data is migrated
mysql -h (hostname, this you will get in your RDS console, under Endpoint Section) -P 3306 -u username -p password
1.) use databasename
2.) show tables;
You should see all the tables which you imported
Upload your codebase in ElasticBeanstalk
Lets suppose your application is PHP based application
You need to zip all the files and upload in Elastic Bean Stalk
Once your upload an deploy is done, A green sign would be shown to indicate everything is fine
You will get the URL of the application (something____elastickbeanstalk.com)
Now we will use Route53 to route our application to this URL
Click on Create Hosted Zone
 |
| Enter domain Name which your purchased from GoDaddy |
All Name server will be shown here, So you would need to add all name servers to put in DNS(GoDaddy)
After Adding Name Servers in DNS























No comments:
Post a Comment